Recommended Sonicwall Firewall Settings
Gain an understanding of how to set up your Sonicwall Firewall for VoIP services.
Table of Contents
Internet connections that are heavily utilized will experience call quality degradation and an overall poor experience with hosted voice. Like most hosted VoIP solutions, SpectrumVoIP’s services work best with consistently low ping times and 60-90 kbps per concurrent phone call.
This document provides guidance for configuring a SonicWALL for SpectrumVoIP services. Included are instructions for traffic prioritization. This uses features within the SonicWALL firewall to appropriately prioritize VoIP-related traffic above all other Internet traffic to help ensure a positive experience.
Recommended Adjustments
Before learning how you can optimize your Sonicwall's settings for use with VoIP reliant devices, it is recommended to read the sections below to review the different adjustments suggested by our team, such as ports and subnets to allow traffic to use, bandwidth requirements, and more.
Subnet and Port Configuration
Read the sections below to allow traffic from the services in use by your company. If you not using a specific service, such as Stratus users that do not use our Enswitch platform and vice versa, you can avoid opening the ports used by that service.
Note: If you are not sure which services you are using and which ports and subnets should be opened, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
SpectrumVoIP Public Subnets
- 199.71.209.0/24
- 24.227.249.0/25
- 72.249.136.32/28
- 206.123.122.32/27
- 212.69.157.32/27
- 40.143.31.64/27
- 45.41.5.0/24
- 12.150.91.0/24
Ports - Stratus Platform
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing our Stratus platform. If you are using our Enswitch (ES) platforms, these ports do not need to be opened.
If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the SpectrumVoIP Stratus mobile app, StratusMEETING, or StratusWEB PHONE, the ports/subnets for those services do not need to be allowed or opened.
If you are not sure which services you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
Main Utilized Ports
- 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
- 20,000-40,000 UDP - RTP
- 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Portal Dynamic Updates
- 8001 - TCP
Text-to-Speech Services - TCP and UDP
- 35.175.185.150:3001
- 35.175.185.150:8000
- 44.212.88.215:8000
- 54.149.243.27:3001
- 54.149.243.27:8000
- 54.70.235.134:3001
- 54.70.235.134:8000
StratusFAX 2.0 - TCP
- 5066 TCP - HTTPS and HTTP
REMINDER: If your company does not pay for and use StratusFAX 2.0, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
StratusHUB Desktop App - TCP
REMINDER: If your company does not use the StratusHUB desktop app, the IP address for this service does not need to be whitelisted.
- 199.71.209.150:8082 - TCP
StratusMEETING - TCP and UDP
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusMEETING, the subnets for this service do not need to be allowed.
- 54.188.133.147:3443
- 3.130.158.184:3443
- 35.183.150.146:3443
StratusWEB PHONE
REMINDER: If your company does not use StratusWEB PHONE, the port for this service does not need to be opened.
- 9002 - TCP - websockets
Ports - Enswitch 1 and 2 Platforms
IMPORTANT: These ports only need to be opened if you are utilizing one of our Enswitch (ES1 or ES2) platforms. If you are using our Stratus platform, these ports do not need to be opened.
If you are not sure which service you are utilizing, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for more information.
- 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
- 10,000-20,000 UDP - RTP
- 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Push Notifications Ports
IMPORTANT: If your users are using our softphone mobile apps on cellular devices or tablets connected to the office's Wi-Fi network, it is recommended to open these ports on the firewall equipment so that push notifications for the apps are not blocked.
Android and Google Devices - Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging, aka FCM
- 443, 5228, 5229, 5230 - TCP
More Info: Ports 5228, 5229, and 5230 are the primary ports used by Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) service for mobile devices to receive push notifications.
Apple Devices - Apple Push Notification Service, aka APNs
- 5223, 443, 2197 - TCP
More Info: Port 5223 is the primary port for communication used by Apple's Push Notification Service (APNs).
Ports 443 and 2197 are used for sending notifications from Mobile Device Management (MDM) software to APNs and as a fallback on Wi-Fi if port 5223 cannot be utilized.
Bandwidth Requirements
Voice-only applications utilize G.711 U-Law as the primary codec and require 87.2 kbps of bandwidth per active call.
It is recommended to round the requirement up to 100 kbps to account for signaling and overhead.
For Example… A 10Mbps/1Mbps ISP connection solely dedicated to the phones would support 10 concurrent phone calls.
Assign a Voice VLAN to Phones
Creating a dedicated VLAN for your different groups of IP devices, such as your desk phones, is a great way to simplify managing your network and troubleshooting future issues with those devices. It is generally recommended to use VLANs to isolate IP devices to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to these devices and limit the spread of potential threats within your network. Segmenting a network using VLANs can also help reduce congestion and improve a network's overall performance, which can be a great boon for networks with many VoIP devices.
Many models of gateways and network switches allow you to automatically place VOIP devices on a dedicated VLAN. There are several ways to accomplish this:
Manual/Static Port Configuration
This is the most basic method, requiring explicit, per-port configuration by a network administrator. It is typically used when automated discovery is not available or desired. The switch port must be configured as an access port with a specific voice VLAN setting. The switch is explicitly told to use a specific Data VLAN for untagged traffic (for the connected PC) and a specific Voice VLAN for tagged (802.1Q) traffic. Any traffic arriving on that port that is untagged is placed into the Data VLAN, and any traffic tagged with the Voice VLAN ID is placed into the Voice VLAN. The IP phone must be manually configured (or use a secondary method like DHCP) to tag its voice traffic correctly.
Note: If you choose this method, please provide your installer with the VLAN ID you wish to use so they can add that parameter to your devices' network settings.
Automatic Discovery via LLDP/CDP
If your network switches support Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and/or Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), Grandstream, Yealink, and Polycom desk phones are compatible with these protocols and can utilize them to be discovered by neighbor devices and switches.
If your network switch does offer LLDP, LLDP-MED, or CDP, it is recommended to ensure these protocols are enabled and configured to point to your desired VLAN. Doing so will allow the switches to discover compatible IP phones and set the devices in a VLAN dynamically depending on the device's configuration information.
What is LLDP-MED?
LLDP-MED is an extension of LLDP that operates between IP phones and network devices, such as switches for voice over IP (VoIP) applications. It does this by sending TLVs.
TLVs (Type-Length-Value) are attributes that describe type, length, and value. Devices that support LLDP can use TLVs to receive and send information with neighboring devices. The information shared using this protocol can be configuration information, device capabilities, and device identity.
Switches that have LLDP-MED enabled can use specialized TLVs that describe discovery capabilities, supported network policies, Power over Ethernet (PoE) capability, and inventory management. This can make connecting and managing IP devices, such as our desk phones, more streamlined.
Option 132 for Yealink Phones
Option 132 in DHCP is a feature that enables automatic VLAN assignment. When a device connects to the network, it sends a DHCP request containing its MAC address. The DHCP server that has Option 132 configured identifies the device and assigns a suitable VLAN.
NOTE: This only works for Yealink brand phones and needs to be made as a custom option on a DHCP Server.
To create a DHCP VLAN option on your DHCP server to allow Yealink phones to automatically connect and provision when plugged in, the following can be configured:
- Option 132: Set Voice VLAN ID
- Type: String (ASCII)
- Value : 'VLANTAG' for example '20' for VLAN 20
This DHCP option should be applied to your native DHCP server so that the phones receive the configuration when first plugged in. This may also be applied to the voice VLAN if needed.
Configure Your Sonicwall's VoIP Settings
SonicOS includes VoIP configuration settings on the VoIP → Settings page.
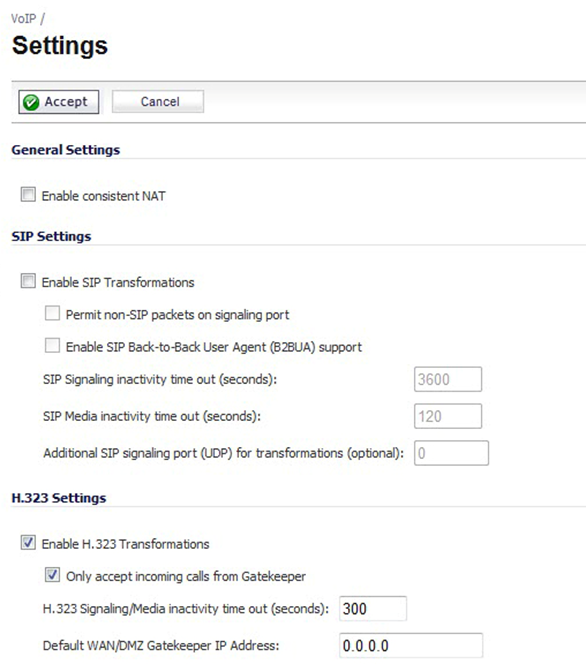
Although there are many settings that can be adjusted on a Sonicwall firewall, this guide will only explore settings that affect the performance of your VoIP services with SpectrumVoIP.
NOTE: Not all settings on this page will be discussed.
If you have any questions about any settings present on your Sonicwall firewall, it is recommended to contact your IT team or Managed Service Provider (MSP) that services your firewall.
Enable Consistent NAT
Enabling Consistent NAT causes a slight decrease in overall security, because of the increased predictability of the address and port pairs. Most UDP-based applications are compatible with traditional NAT; therefore, we recommend enabling Consistent NAT unless your network uses applications that require this disabled.
To enable Consistent NAT, select Enable consistent NAT and click the Accept button. This option is disabled by default.
Disable SIP Transformations
In the Sonicwall's SIP Settings, the Enable SIP Transformations setting is enabled by default. Having this setting enabled can commonly cause quality of service issues with VoIP calls.
It is recommended to disable SIP Transformations to avoid one-way audio and issues with parking and transferring.
To disable SIP Transformations, deselect the Enable SIP Transformations option.

Prioritize SpectrumVoIP Traffic
One of the greatest challenges for VoIP is ensuring high speech quality over an IP network. VoIP and other types of media streaming are very sensitive to delay and packet loss. Managing access and prioritizing traffic are important requirements for ensuring high-quality, real-time VoIP communications.
To prioritize SpectrumVoIP traffic, you must create four Address Objects and combine them into an Address Group, then create firewall rules to allow and prioritize traffic destined for this Address Group.
Step 1: Create Address Objects
- Navigate to Network → Address Objects.
- Click Add to create the following new address objects listed in the table below.
Note: Ensure that the Zone Assignment is set as WAN and Type is set as Network for each.
| Suggested Object Name | SpectrumVoIP Subnets | Netmask |
|---|---|---|
| SpectrumVoIP Subnet 1 | 199.71.209.0/24 | 255.255.255.0 |
| SpectrumVoIP Subnet 2 | 24.227.249.0/25 | 255.255.255.128 |
| SpectrumVoIP Subnet 3 | 72.249.136.32/28 | 255.255.255.240 |
| SpectrumVoIP Subnet 4 | 206.123.122.32/27 | 255.255.255.224 |
Step 2: Add an Address Group
- After creating the address objects above, click Add Group.
- Name the group “SpectrumVoIP Subnets”.
- Add the four, new SpectrumVoIP Address Objects to the group using the right arrow.
Step 3: Create Firewall Access Rules
- Navigate to Firewall → Access Rules.
- In the LAN to WAN rules section, click Add.
- In the General tab, configure the following:
- Service - Set to Any.
- Source - Set to Any.
- Destination - Select the SpectrumVoIP Subnets address group.
- On the Traffic Shaping tab, do the following:
- Egress Bandwidth Management - Enable this function.
- Ingress Bandwidth Management - Enable this function.
-
Bandwidth Priority - Select 0 Realtime for both.
Note: Bandwidth Management will need to be enabled globally to allow the per-firewall rule BWM tab to be accessible.
Step 4: Add a Service Object
- Navigate to Network → Services and click Add.
-
Add a new Service Object with the following configured:
- Name - Type SpectrumVoIP RTP.
- Protocol - Select UDP (17).
- Port Range - Select 20,000-40,000.
Step 5: Create a Service Group
- Select Service Groups → Add Group.
- Give the new service group a Name, such as “SpectrumVoIP Voice”.
- Move the SIP and SpectrumVoIP RTP options the right section using the arrows.
- Click Add.
Use Option 66: Phone Provisioning via DHCP
If your Sonicwall will act as a DHCP server, you can set it to utilize Option 66 to make it simpler to install and provision your desk phones.
Note: If you are interested in setting up Option 66 for the DHCP server of your Sonicwall, contact your Installer or our Technical Support team for further assistance.
When Option 66 is configured, phones that boot up and connect to the Sonicwall will be provided a Provisioning URL. When the phones use the Provisioning URL to connect to our TFTP server, they can request and apply a config file to make setting up and updating themselves more streamlined.
To configure Option 66 for your Sonicwall, this can be done by creating an Option Object in its DHCP Advanced Settings.
- Login to the SonicWall Management GUI
- Navigate to Network → System → DHCP Server.
- Click the Advanced button next to the Enable DHCPv4 Server option.
- On the Option Objects tab of the DHCP Advanced Settings window, click the + Add button.
- Enter the following information:
- Option Name: Enter a name for this object, such as “Option 66”.
- Option Number: Select 66 (TFTP Server Name)
-
Option Value: Enter the URL for our provisioning server provided by a SpectrumVoIP Installer or Technician.
Note: If you do not have this URL, contact your SpectrumVoIP Installer or our Technical Support team for further assistance.
- Click the Save button.
✔ Once you have created an Option 66 Option Object, you can assign it to existing DHCP Server Lease Scopes that are assigned to subnets your desk phones will be connected to.
Quality of Service
QoS encompasses a number of methods intended to provide predictable network behavior and performance. Network predictability is vital to VoIP services. QoS, when configured and implemented correctly, can properly manage traffic and guarantee the desired levels of network service.
✔ SonicOS includes QoS features that add the ability to recognize, map, modify and generate the industry-standard 802.1p and Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCP) Class of Service (CoS) designators.
Manage Bandwidth on a WAN Interface
WARNING: Voice-only applications utilize G.711 U-Law as the primary codec and require 87.2 kbps of bandwidth per active call. It is recommended to round the requirement up to 100 kbps to account for signaling and overhead.
The bandwidth specified should reflect the actual bandwidth available for the link. Oversubscribing the link (declaring a value greater than the available bandwidth) is not recommended.
Enable VoIP Logging
You can enable the logging of VoIP events on the Log → Settings page. Log entries are displayed on the Log → Monitor page. To enable logging of VoIP, see Log → Settings.